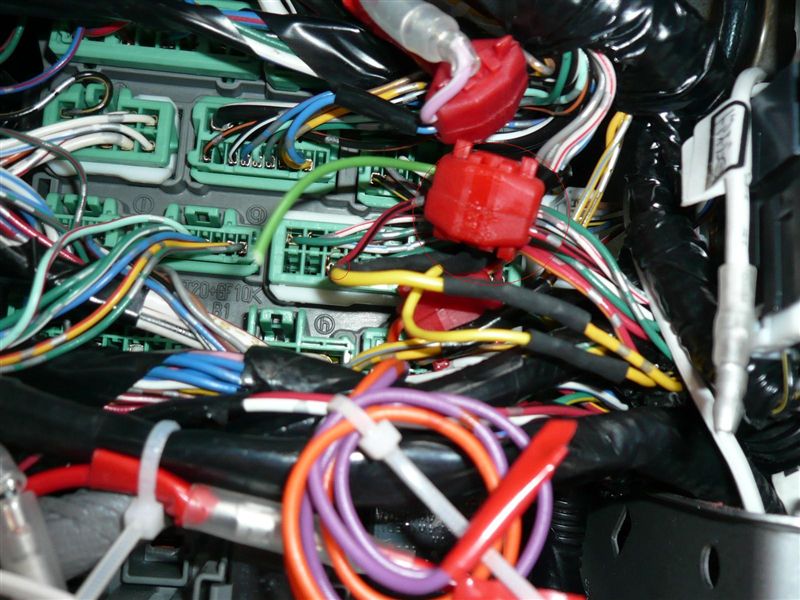
Failure Analysis of Automotive Mounting Clips
Ensuring the lifespan of automotive fastening systems requires a deep understanding of potential failure factors. Most fastener problems can be traced back to thermal degradation, mechanical stress, or fatigue caused by vibration.
Thermal Embrittlement and Material Selection
Standard polymers often experience molecular chain breakage when continuously exposed to the high temperatures of the engine compartment, leading to embrittlement and catastrophic fracture.
Cause: Continuous operating temperatures exceeding the glass transition temperature of standard plastics.
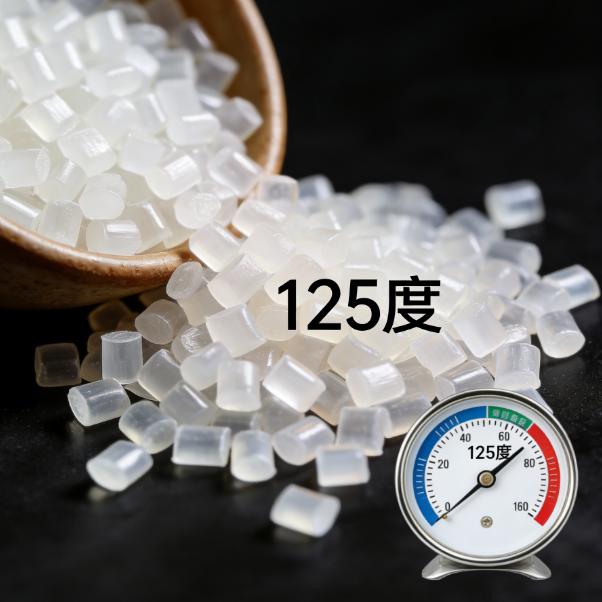
Solution: Use high-performance, thermally stable materials such as PA66-HS or PA46. These materials are specially designed to maintain impact strength and flexibility at constant temperatures up to +125°C or +150°C.
Handling Stress and Precision Molding
Structural failures occurring during assembly are often due to localized stress concentrations.
Cause: Excessive insertion force (IF) requirements due to poor tolerance control or non-ergonomic clip geometry.
Solution: Employ precision injection moulding processes with tolerances controlled to ±0.05 mm to ensure uniform load distribution. Optimised geometry reduces initial drag, minimizing the risk of microcracks during high-speed automated assembly.

Dynamic Fatigue and Stability Maintenance
In the high-vibration automotive environment, creep and fretting wear can damage the locking mechanism of the snap-fit over time.
Causes: Insufficient pull-out force (EF) design or loss of material elasticity leads to minute displacements, resulting in wear on the locking interface.
Solutions: Strategically use reinforcing ribs and adjust material elasticity. By maintaining a high pull-out force/insertion force ratio (EF/IF), the snap-fit ensures the harness is securely held, even under continuous harmonic vibrations.
Conclusion
In automotive manufacturing, small components can have system-level consequences. A single mounting clip failure can result in harness damage, electrical faults, or costly service actions.
LHE designs automotive mounting clips with a focus on real-world operating conditions. By combining material expertise, controlled manufacturing processes, and application-driven design, LHE supports stable wire harness routing across chassis, interior, and powertrain systems.
From high-voltage EV platforms to conventional vehicle architectures, LHE provides fastening solutions that align with current automotive production requirements and evolving mobility technologies.